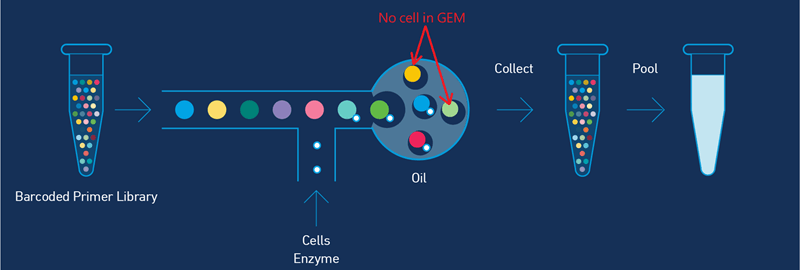
10x Genomics Single Cell RNA Sequencing
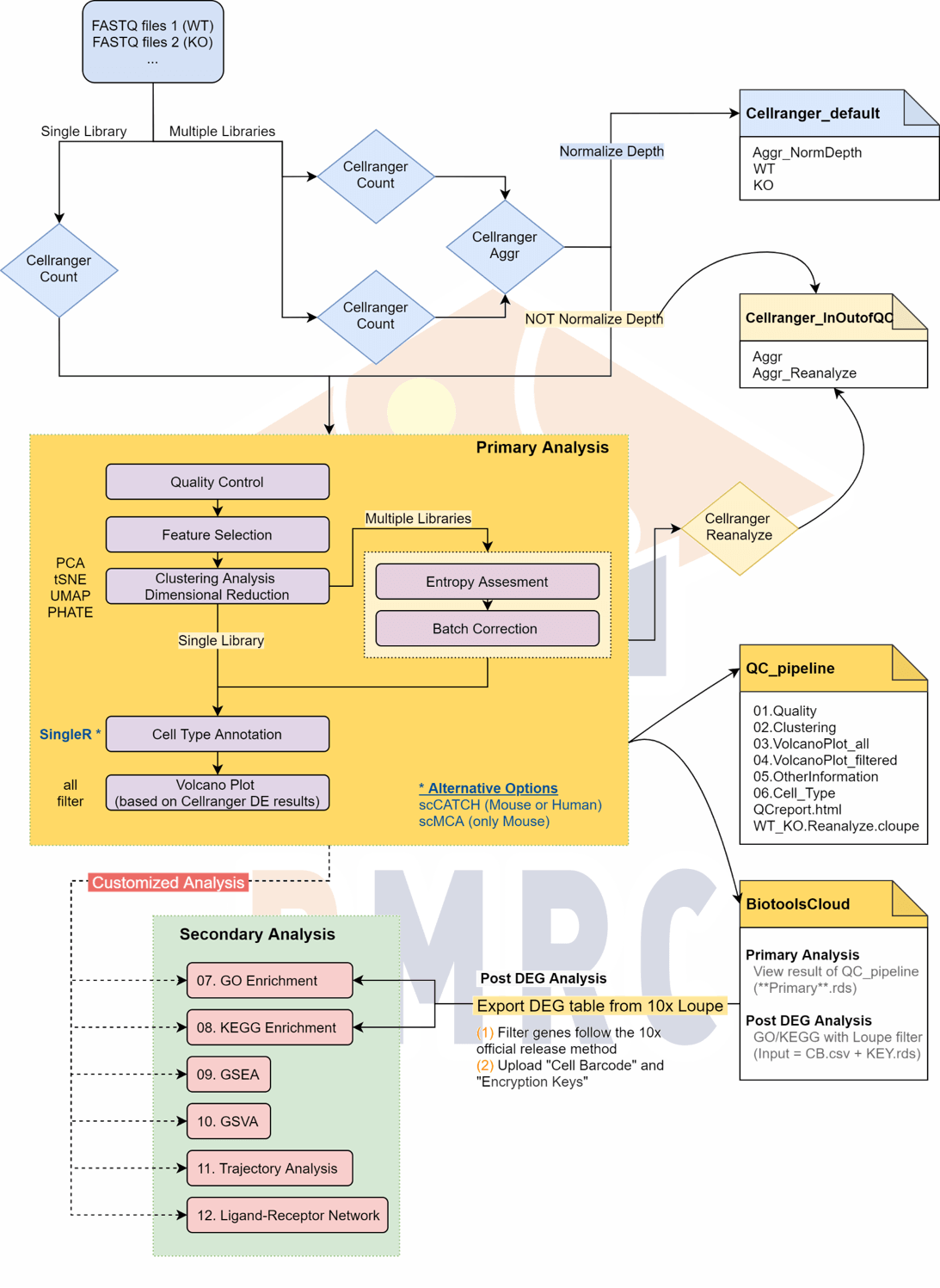
技術原理
樣品需求
建議上機細胞數: 16,000 顆,搭配60G定序數據量*
*根據10x Genomics 原廠建議,每顆細胞最低需要 20,000 read pairs,增加上機細胞數,數據量也需要酌量提升
考慮建庫過程中損耗,建議提供兩倍以上的細胞量,視細胞種類及製備情況調整,請洽當區業務,將有專人協助評估樣品製備流程
10x Genomics 原廠樣品製備說明範例
單細胞懸浮液 (Single Cell Suspension)製備建議
Cell Preparation for Single Cell Protocols
組織分離及特定細胞族群分離製備建議
Enrichment of CD3+ T Cells from Dissociated Tissues for Single Cell RNA Sequencing and Immune Repertoire Profiling
腫瘤組織單細胞分離製備建議
Tumor Dissociation for Single Cell RNA Sequencing
細胞培養分離製備建議
Single Cell Suspensions from Cultured Cell Lines for Single Cell RNA Sequencing
死亡細胞移除製備建議,適用於經過分選的細胞樣品, Cell sorting by flow cytometry or Magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS)
Removal of Dead Cells from Single Cell Suspensions for Single Cell RNA Sequencing
小鼠胚胎神經組織樣本製備建議
Dissociation of Mouse Embryonic Neural Tissue for Single Cell RNA Sequencing
單細胞及細胞核分離製備建議
Isolation of Nuclei for Single Cell RNA Sequencing & Tissues for Single Cell RNA Sequencing
Single Cell RNA雲平台- 線上分析工具
▶ 任你自由調整的篩選門檻與參數 線上調整樣品名稱,更動細胞數篩選及分群的各個門檻
▶ 把圖變成你喜歡的顏色與形狀 直接在平台上調整製圖大小、標題、顏色、字體
提供多種下載格式,製作報告好簡單
▶ 批次效應評估與校正
提供多項套件,修正批次效應影響的細胞分群
▶ 最豐富的分析項目
差異基因分析、基因富集分析(GO、KEGG)、細胞類型標記 (人類及小鼠)
偽時間分析視覺化呈現等,套件持續更新
▶ 深度整合Loupe Cell Browser,讓分析結果最大化
直接匯入差異基因列表,清楚解析基因功能
觀看scRNAseq雲平台直播影片
圖爾思雲平台入口
進階分析項目
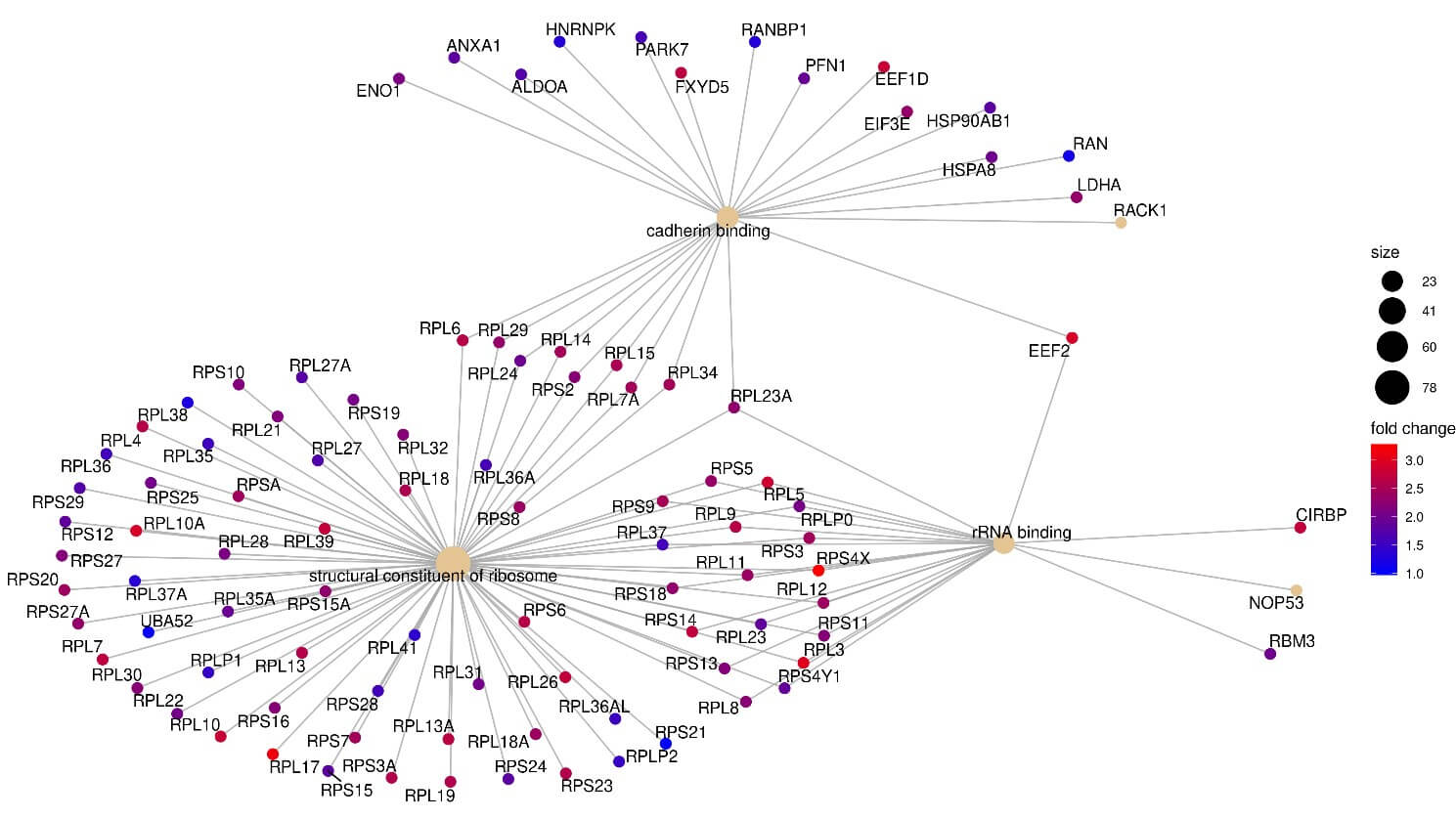
- GO
篩選差異基因,分析差異基因功能路徑。
(* 雲平台匯入Loupe 差異基因計算結果,可匯入第一階段分析不另行收費)
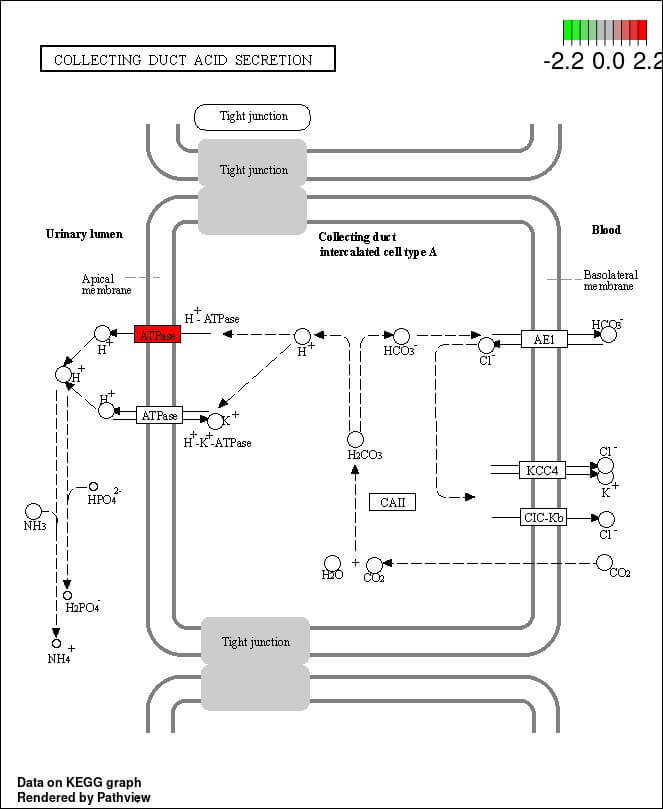
- KEGG
篩選差異基因,分析差異基因參與之代謝路徑。
(* 雲平台匯入Loupe 差異基因計算結果,可匯入第一階段分析不另行收費)
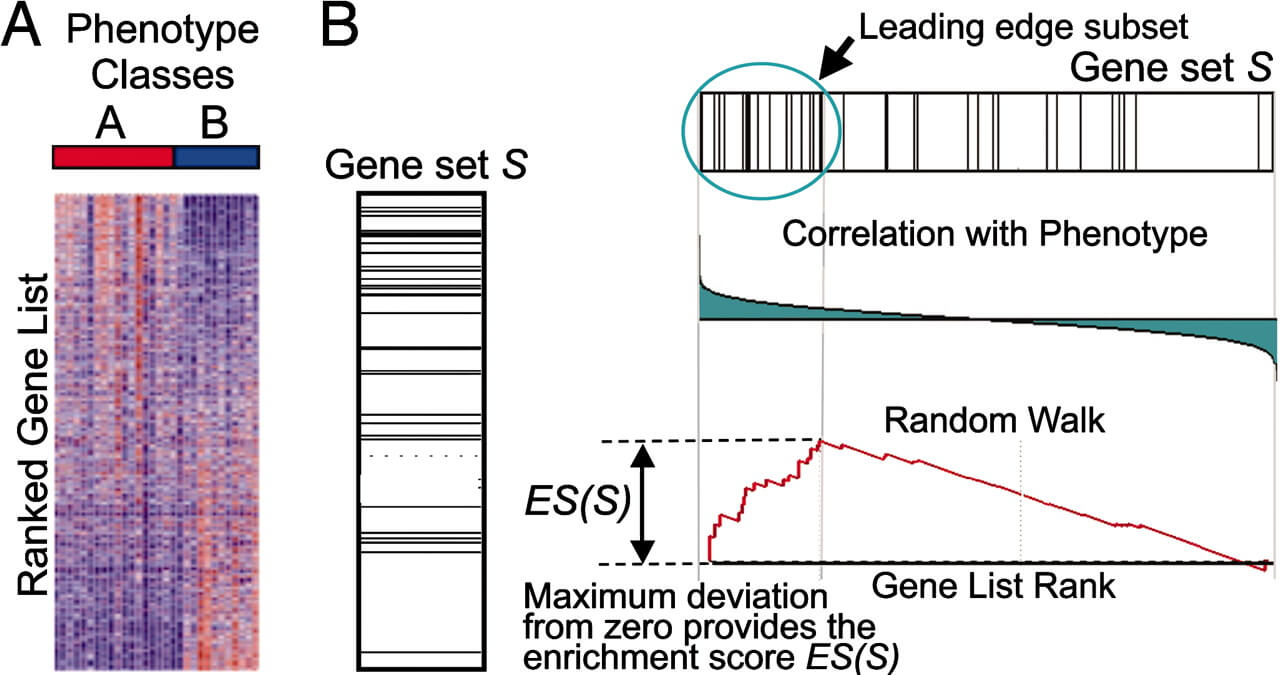
- GSEA
不篩選差異基因,DEG fold-change進行排序後,與預先定義的基因集相比,找出「差異不明顯但趨勢一致」的功能基因集。
(詳見:次世代定序知識櫥窗http://toolsbiotech.blog.fc2.com/blog-entry-118.html)
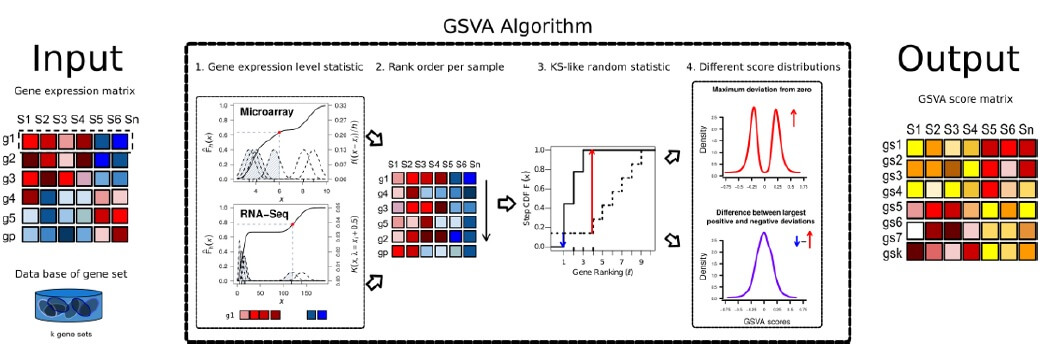
- GSVA
不進行差異基因分析,以單顆細胞為單位對每個基因進行表現量排序,並依照「排序值」、「基因是否在預先定義的基因集內」計算GSVA分數;最後可得「基因集(基因集內所有基因的綜合表現量)-細胞」之分數矩陣。配合tSNE/ UMAP plot,若觀察到一群細胞聚類且GSVA分數高,則意味著此群細胞相比其他細胞群具有此基因集富集。
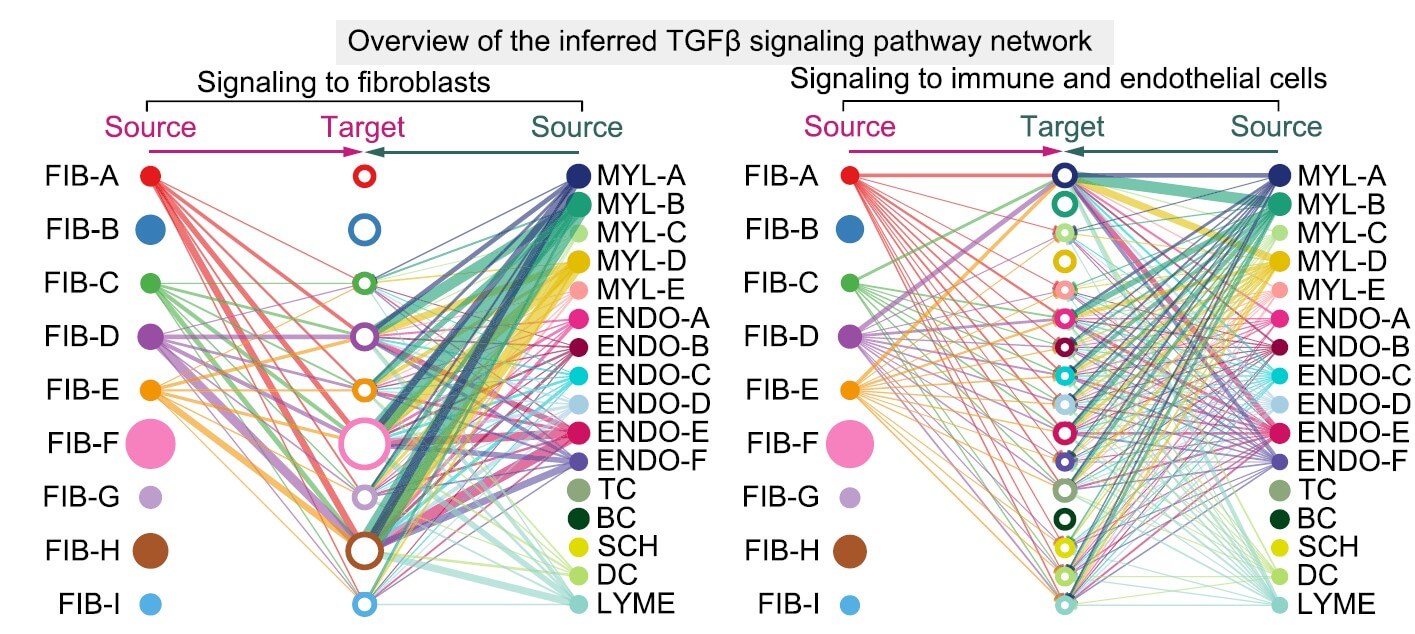
- LR-network
利用Ligand-Receptor判斷細胞群之間的互動性。
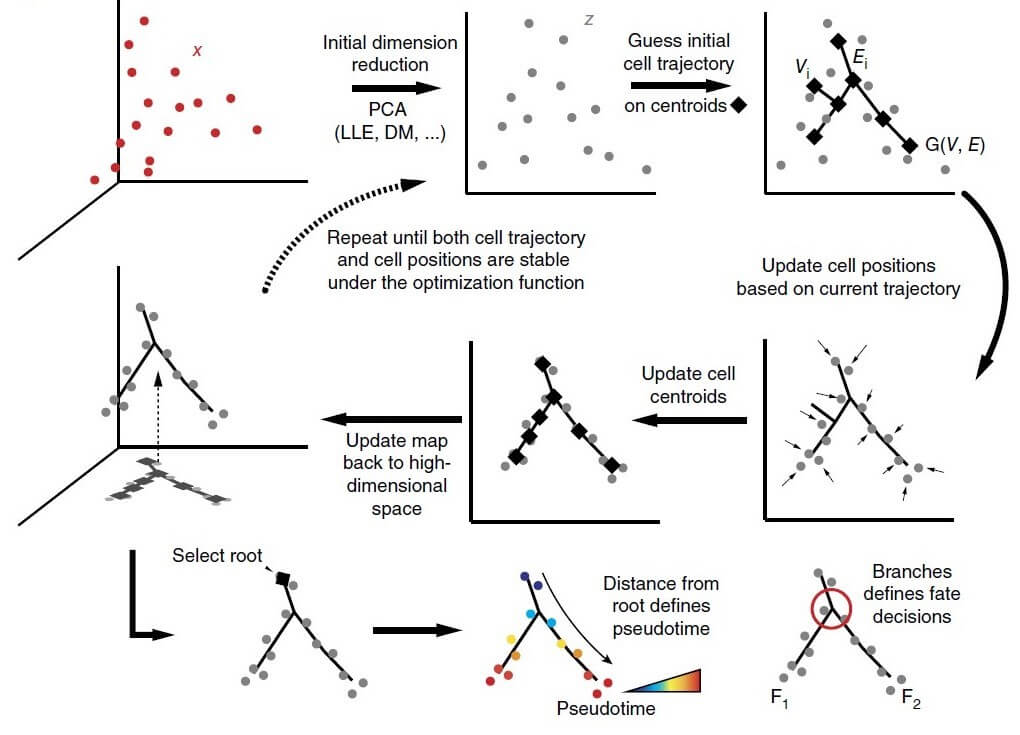
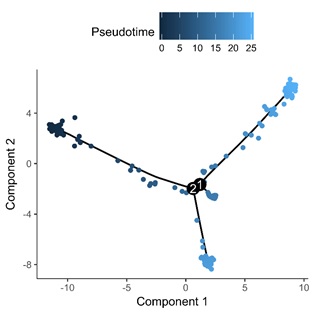
- Trajectory
「模擬」細胞演化之軌跡,輔助推測細胞可能的遷移性。
(* 雲平台提供客製化計算結果之視覺化呈現)
參考資料:
[1] Gene Ontology, C., The Gene Ontology project in 2008. Nucleic acids research, 2008. 36(Database issue): p. D440-D444
[2] Yu, G., et al., clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics, 2012. 16(5): p. 284-7.
[3] Kanehisa, M., et al., KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res, 2008. 36(Database issue): p. D480-4.
[4] Kanehisa, M., et al., New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019. 47(D1): p. D590-d595.
[5] Subramanian, A., et al., Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2005. 102(43): p. 15545.
[6] Hänzelmann, S., R. Castelo, and J. Guinney, GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013. 14(1): p. 7.
[7] Jin, S., et al., Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nature Communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 1088.
[8] Qiu, X., et al., Reversed graph embedding resolves complex single-cell trajectories. Nature Methods, 2017. 14(10): p. 979-982.